Meet cichlids: These fish are doting parents, builders, and dancers
The unique diversity of cichlids in Africa’s oldest lake could help unlock the secrets of evolution.
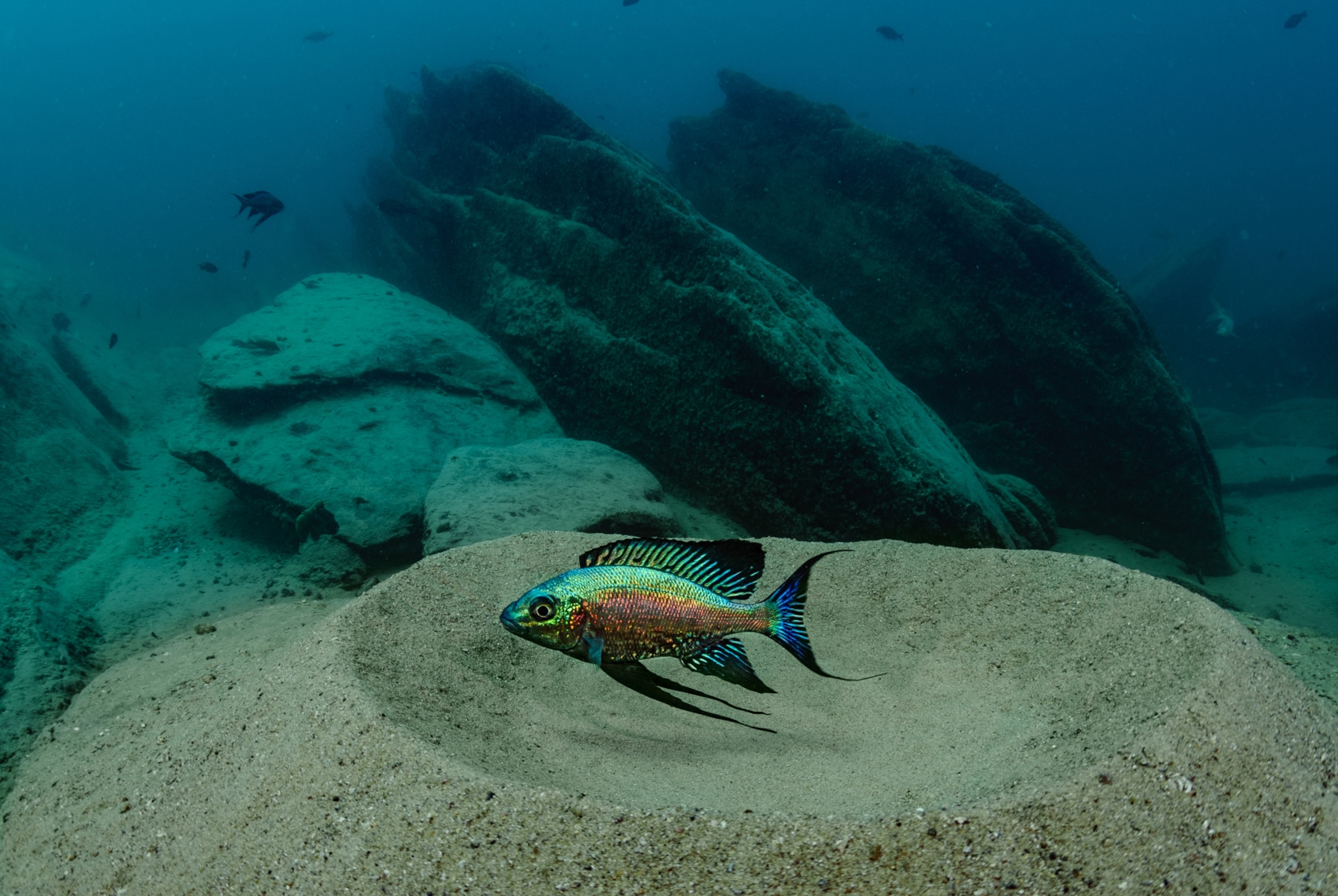
Nothing about cichlids is ordinary. In Lake Tanganyika alone, at the divide between Central and East Africa, roughly 250 species evolved from a single ancestor over 9.7 million years.
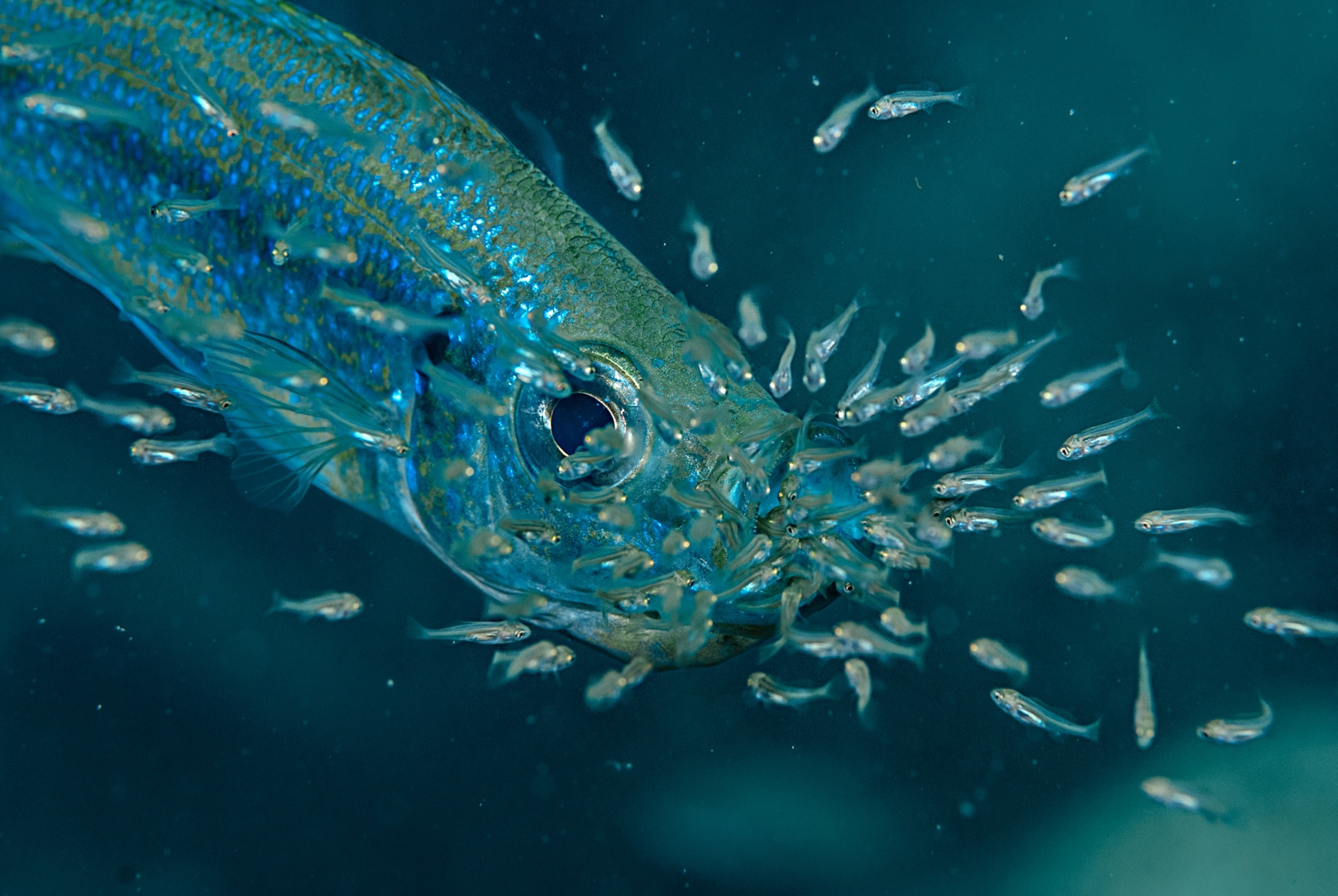
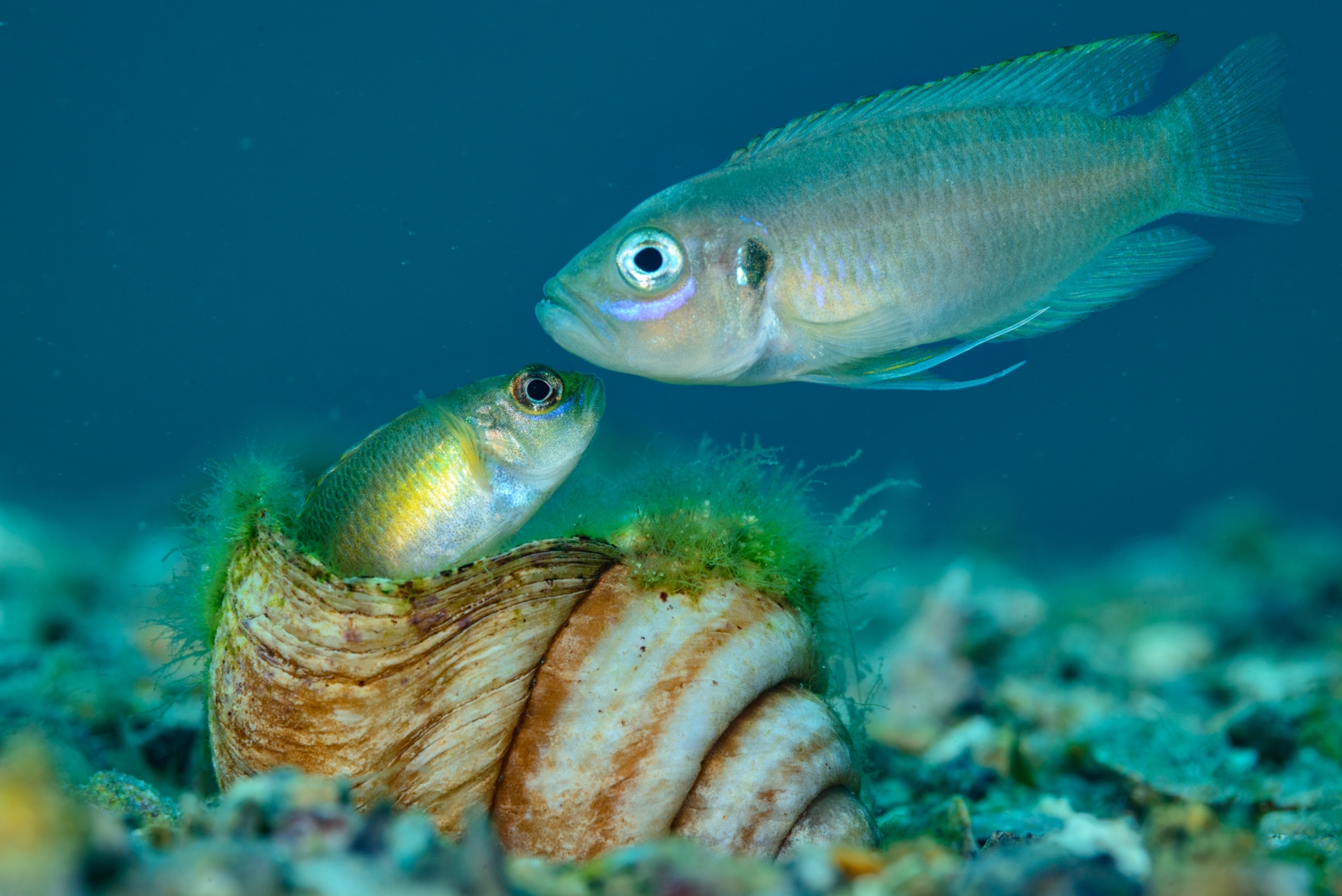
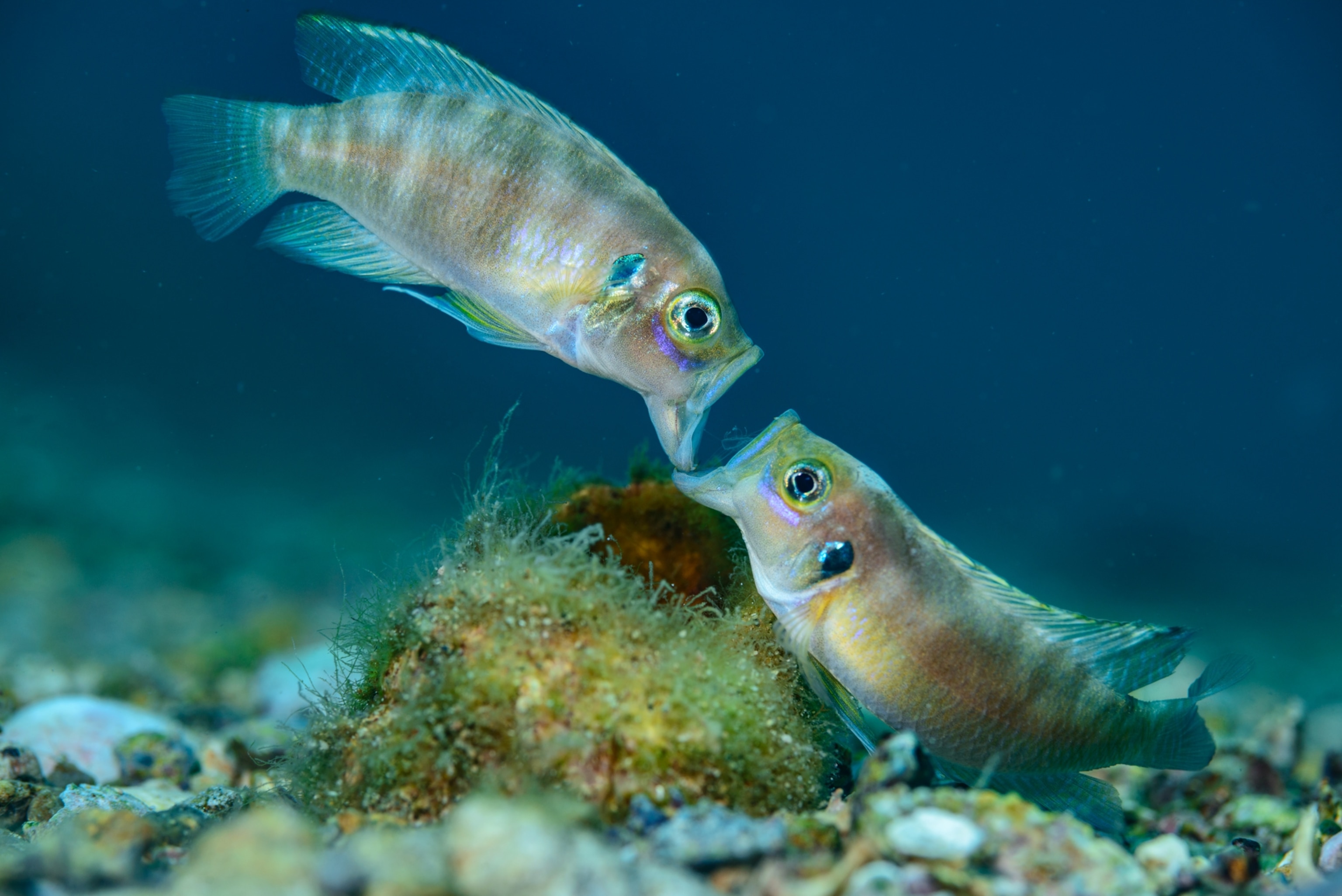
Some are the size of a preschooler; others, no longer than a pinkie finger. Some spend their lives searching for and defending the perfect shell or building elaborate sand stages on which to attract a mate. Others thrive in harems. Many are doting parents to their young fish—though sometimes they eat their own eggs. In a clear example of explosive diversification, cichlids (SICK-lids) have adapted to fit almost every niche in the lake.
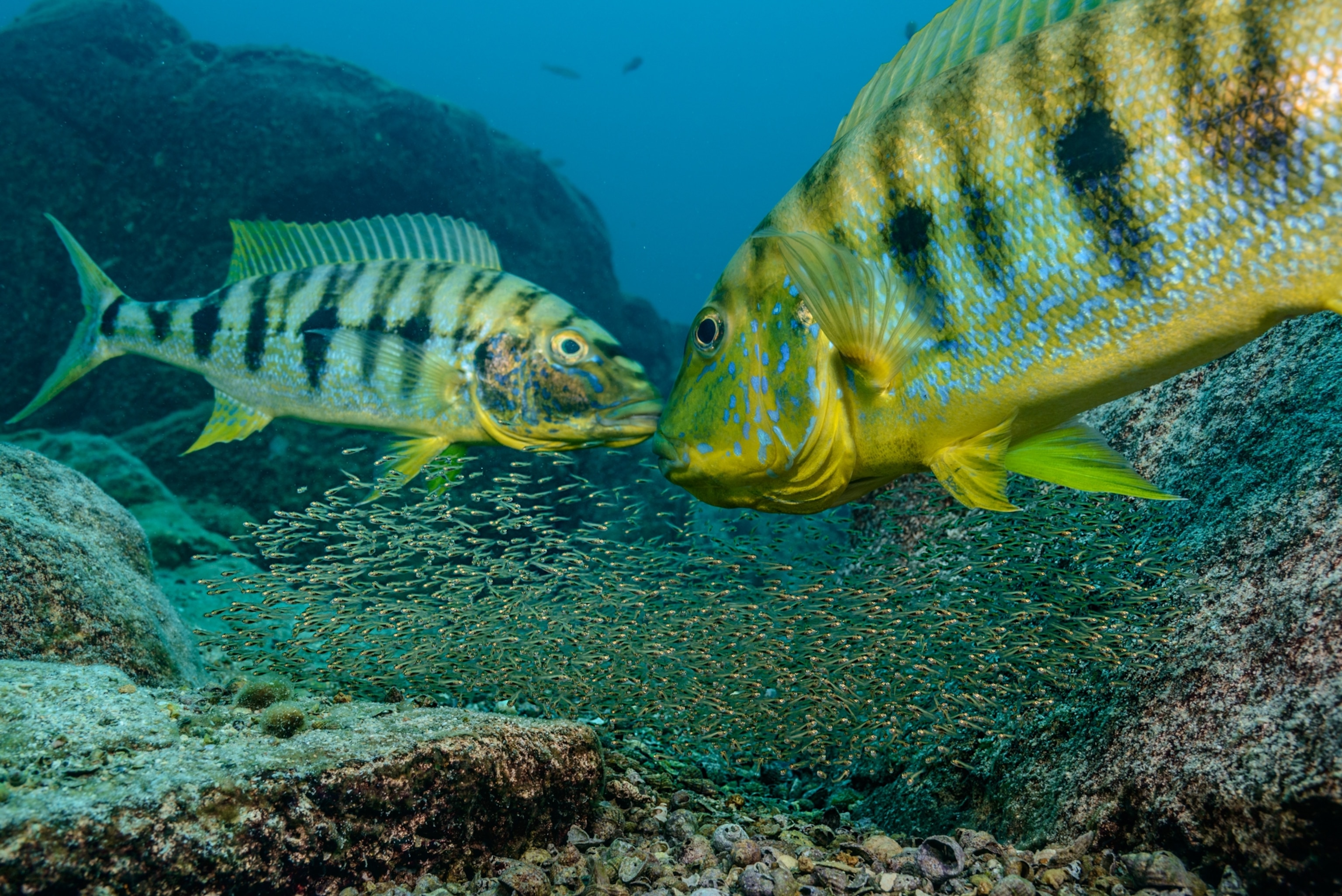

The majority of cichlids there are found nowhere else, and they offer scientists clues to unlocking the secrets of evolution. It’s an urgent endeavor: Animals are going extinct before we’ve learned how they came to exist.
The fish face myriad threats: Urban development degrades their water; gill net fishing depletes populations. The most beautiful are coveted for the aquarium trade; many die in transport.
Cichlid expert Walter Salzburger, at the University of Basel in Switzerland, hopes that growing scientific interest in the fish will spur conservation efforts. “Protecting cichlids,” he says, “means protecting the entire ecosystem of this ancient lake.”



This story appears in the February 2022 issue of National Geographic magazine.




