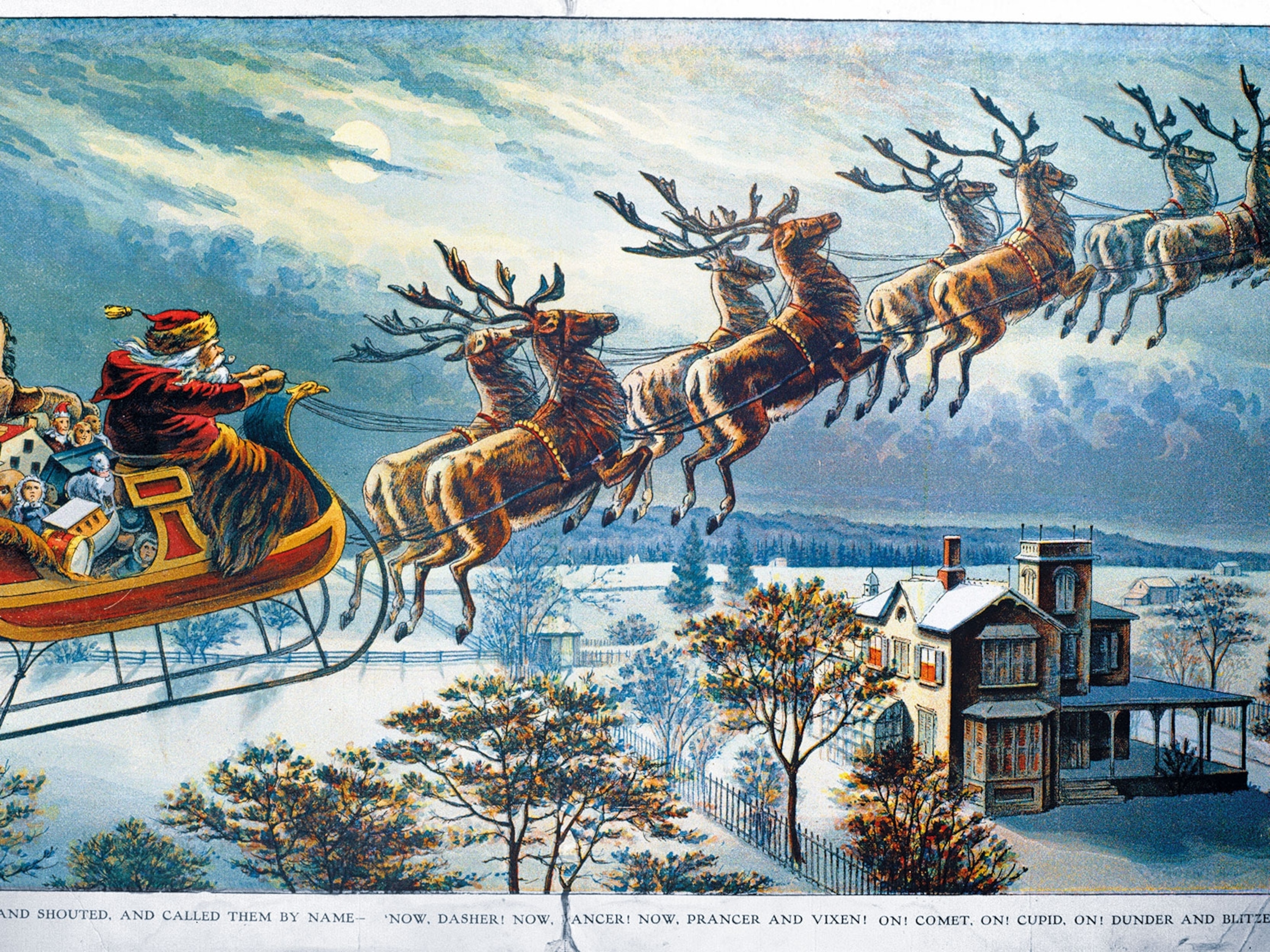
Forget 'walking the plank.' Pirate portrayals—from Blackbeard to Captain Kidd—are more fantasy than fact.
How we think famous swashbucklers walked, talked, and dressed didn't come from the history books, so where did these pirate myths come from?
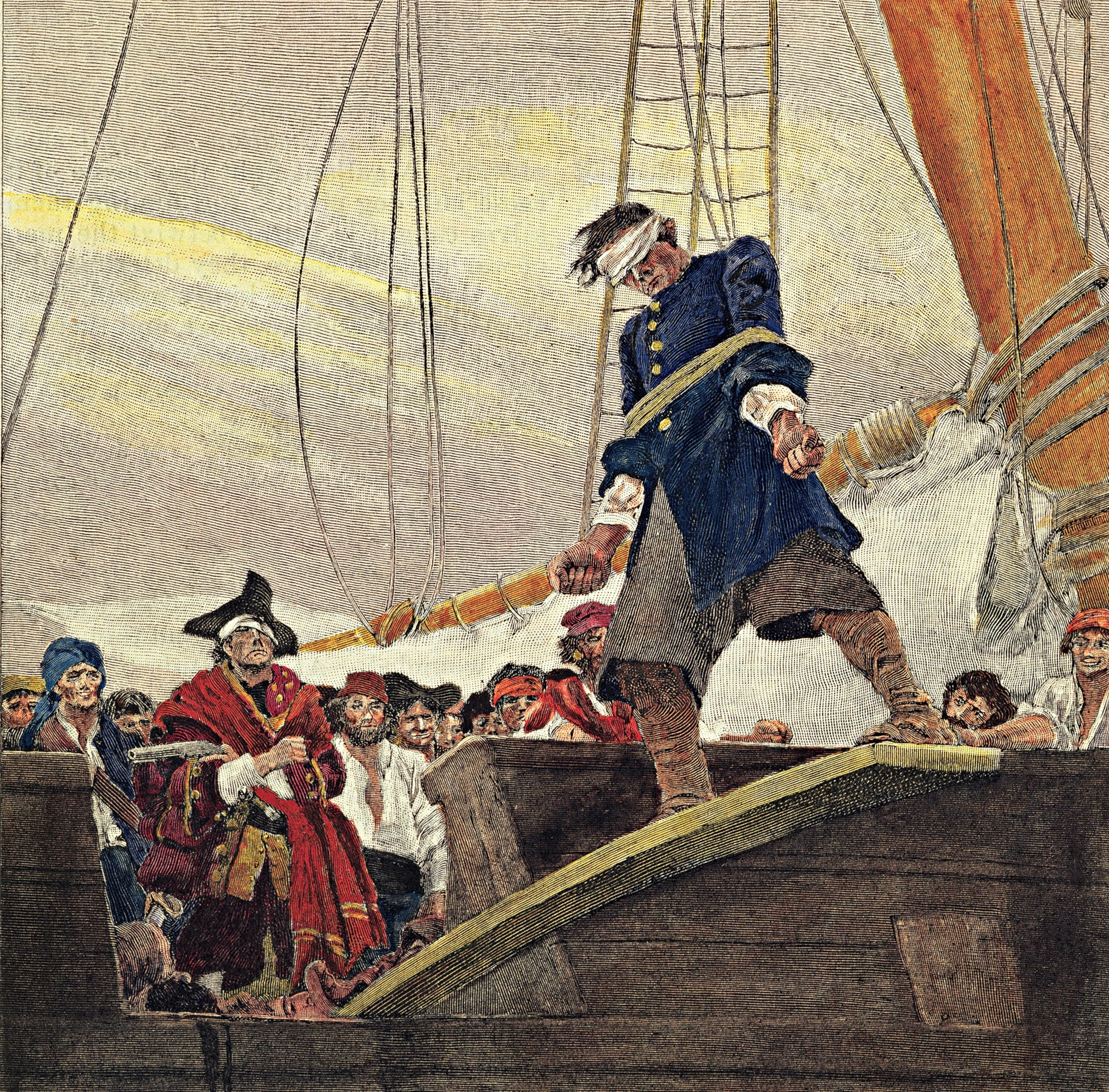

Say “pirate,” and people envision grizzled men with eye patches, parrots, and treasure maps. They picture buccaneers forcing their victims to walk the plank, and crying “Shiver me timbers” as they fly the Jolly Roger flag. It turns out, many of these stereotypes are not true. Pirates have been around for nearly as long as people have sailed the world’s waters, and, in fact, still exist. It’s just how they’ve been depicted that’s often misleading. So where did these misinterpretations come from?

Pirate fashion
Pirates are commonly portrayed wearing colorful attire. He may sport as a loose-fitting shirt with a bandana around his head, a scarf around his waist, ripped pants, wearing tattered boots, like Captain Jack Sparrow from the Pirates of the Caribbean film series. Or he may appear a bit foppish, much like Stede Bonnet, the "gentleman pirate" in the 2022 series Our Flag Means Death.
(Meet pirate queen Zheng Yi Sao, who tormented the South China Sea in the early 19th century.)
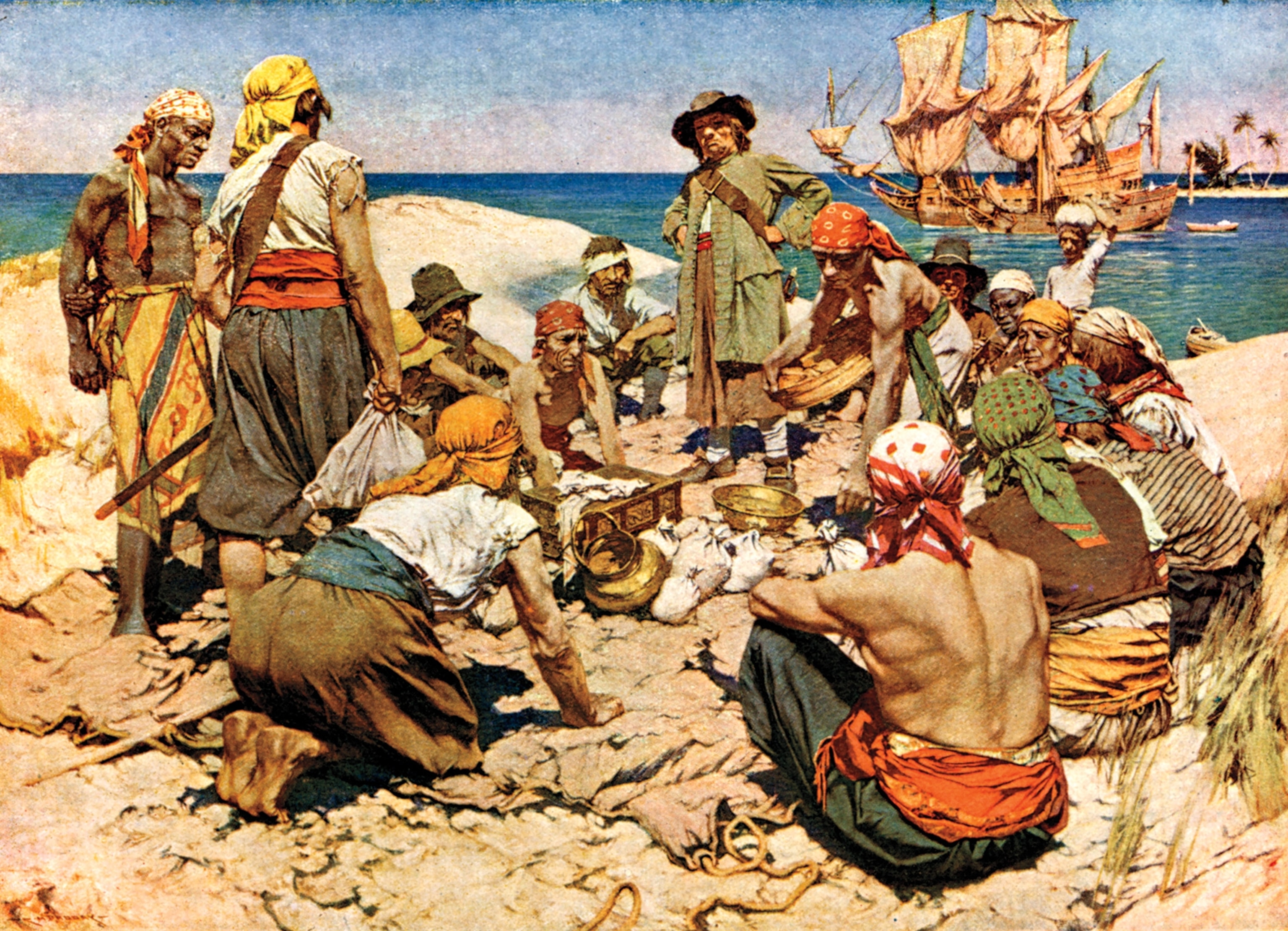

Unfortunately, these looks are just not true. Much of this ostentation came from American artist Howard Pyle, who took his inspiration from Spanish bandits of the late 19th century. Sailors in the 18th century, pirates included, wore things such as loose pants cut off at the knee and thigh-length blouses.
Prosthetic limbs are another common pirate trait. It’s true some pirates had a wooden leg or hook hand, though it probably wasn’t the norm. More often than not, amputations at sea were likely a death sentence. While ships carried medicine chests, and medical care was often meted out by someone on the crew, infection and blood loss could lead to death. Even if a pirate survived an amputation, his ability to fight would be limited. But losing a limb didn’t mean one could not continue on the ship; the person might serve the crew, for instance, as a cook.
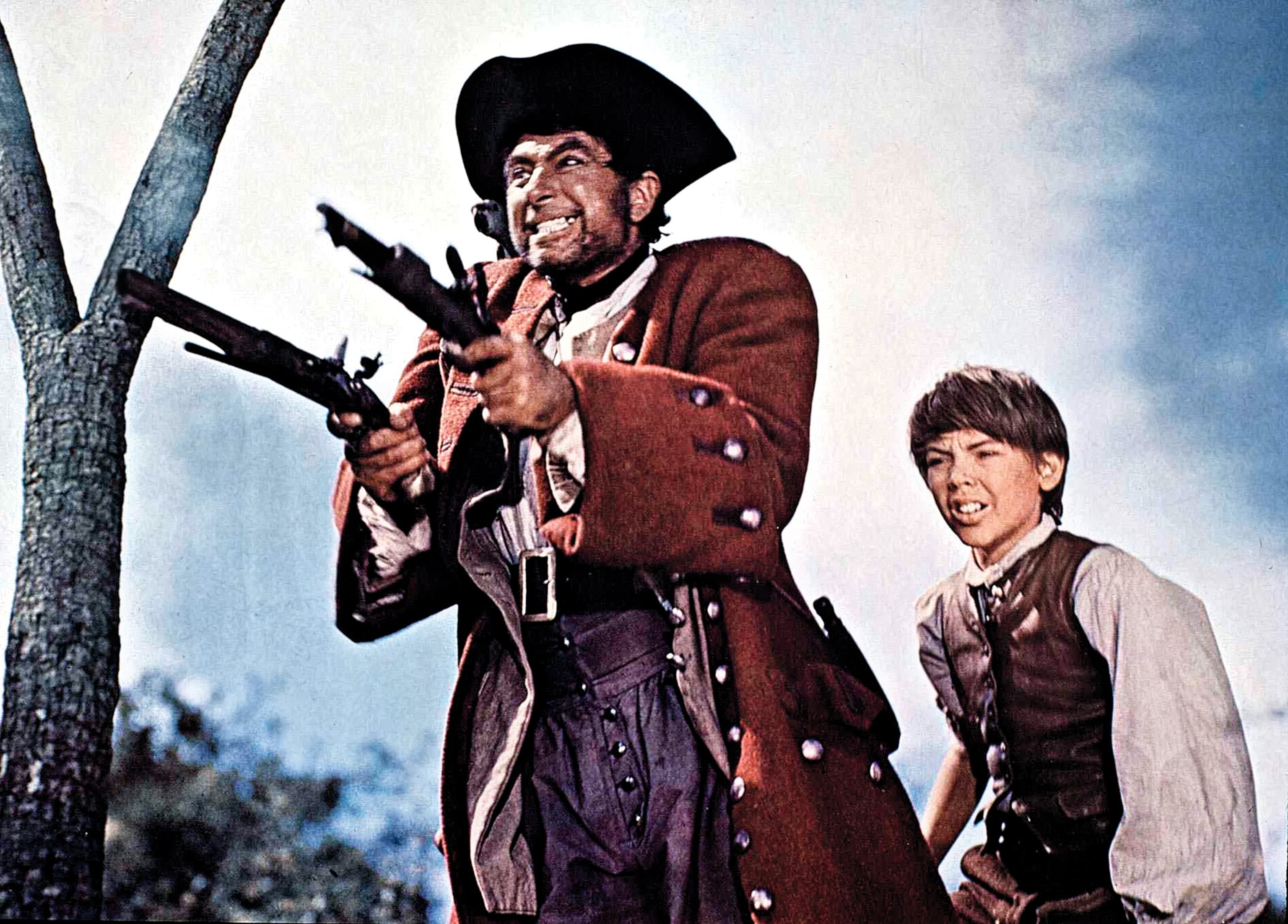

Pirate talk
Common pirate phrases—such as Arrrrr me mateys!” and “Shiver me timbers!”—are common in pirate movies and pop culture. But they’re not legitimate things a pirate would actually have said. Robert Louis Stevenson imagined some of them for his 1883 novel Treasure Island, published more than 150 years after the “golden age” of piracy.
The trope of talking like a pirate is mostly a product of 20th-century Hollywood. In particular, British actor Robert Newton, who played both Blackbeard and Long John Silver. His portrayal of the fictional captain in the 1950s rendition of Treasure Island used an exaggeration of his own West Country accent and would define the sound of a pirate's accent. His portrayal also popularized many of the sayings associated with pirates today. In reality, pirates most probably spoke in a manner similar to all sailors of the time.
(Queen Elizabeth I's favorite pirate was an English hero, but his career has a dark side.)

Treasure, buried or otherwise
Captain Kidd may have buried his treasure, but that was a rare exception for most pirates. Typically, they spent their ill-gotten gains on women and alcohol at pirate-friendly ports as quickly as they could. Burying treasure would be dangerous due to shifting sands and tides, so one might easily lose their treasure. And there was a distinct lack of trust, not knowing if others might deceptively go back to dig up the treasure on their own.
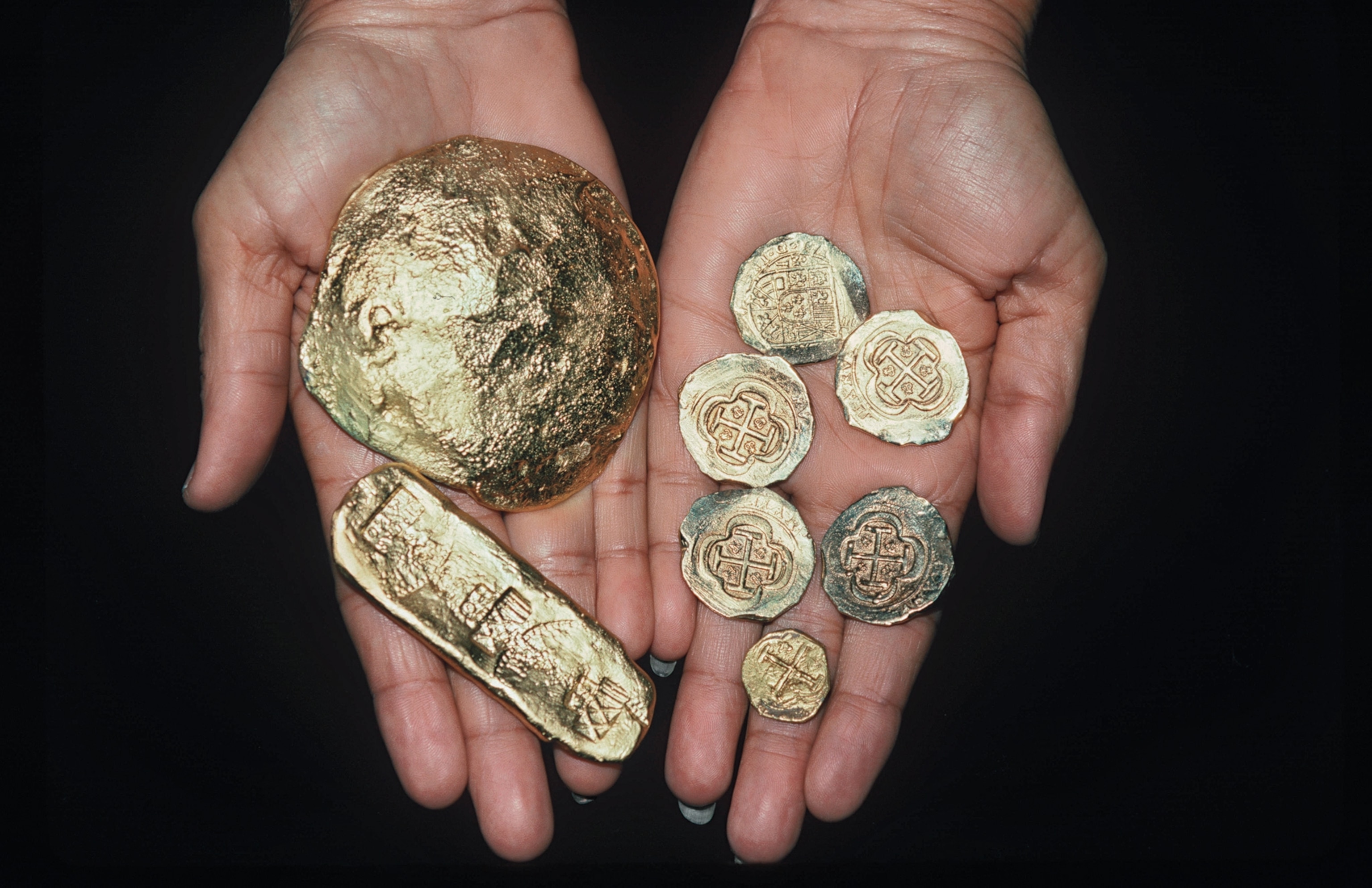
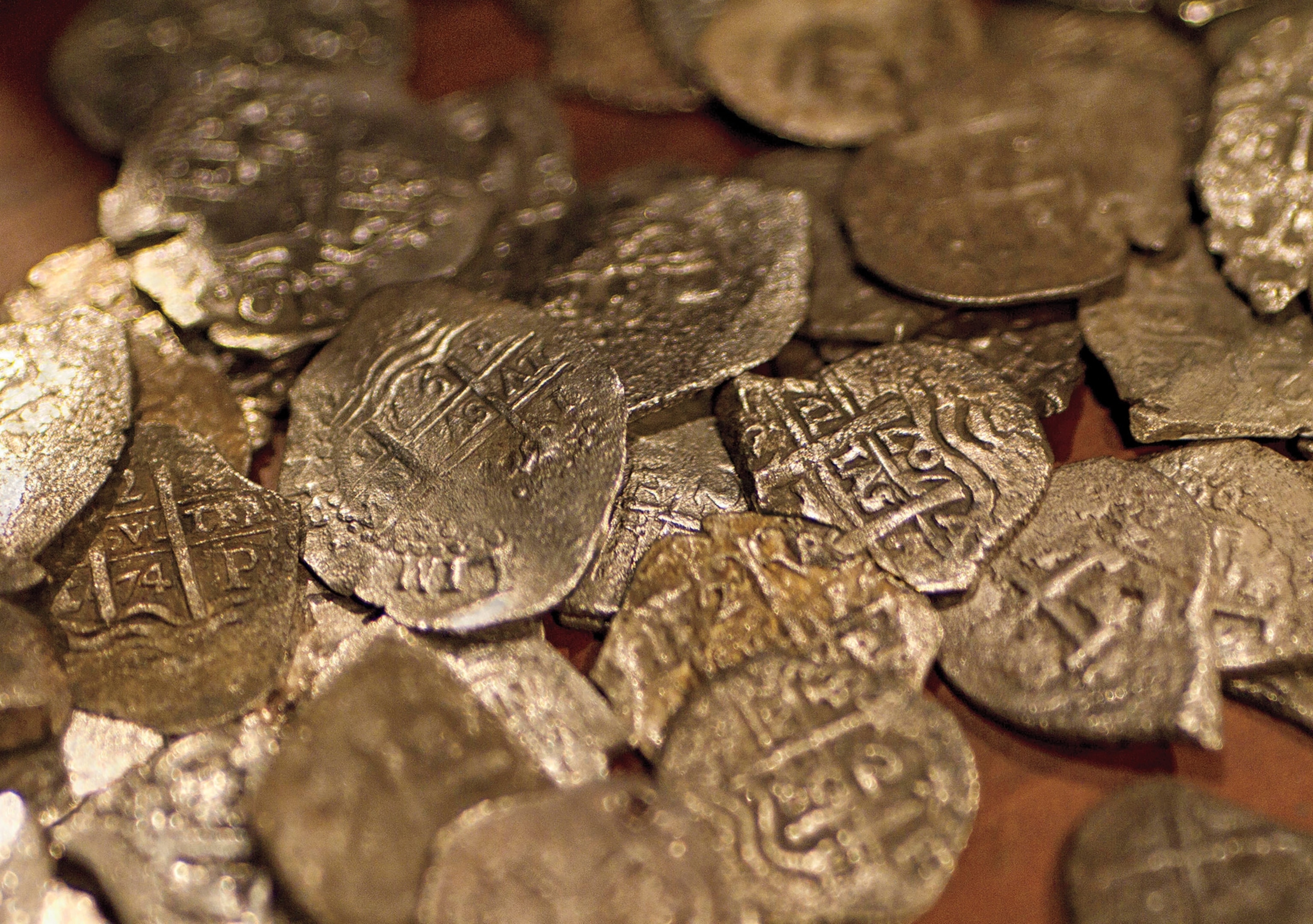
Also, much of the loot pirates collected was not in the form of silver or gold. Such treasure would have been difficult to come by. The more common "booty" would have been whatever goods or commodities they could get their hands on, including timber, furs, silks, cotton, spices, and medical supplies. They also loaded up on items to perform necessary repairs on their ships, including cable, rigging, and sails.
Pirates' booty
Pirate codes
There is evidence that many pirate crews adopted a code of honor or articles of agreement, mostly to keep order on board the ship. These codes dealt with everything from how to divvy up loot, to what happened to pirates if they became injured in the line of duty, to how bad behavior would be dealt with, to how prisoners would be treated. Some pirate articles have survived to this day, including the code of Englishman George Lowther and his crew, which, for example, compensated a person who lost a limb during a skirmish.

If a pirate violated the code, it is unlikely they were made to "walk the plank." Little to no historical evidence exists to support that practice, which was largely pulled from fiction, including Treasure Island. If victims were punished in some way, it was typically via keelhauling. Keelhauling was arguably a more hideous fate that involved an individual being tied to a rope and dragged under the ship. Victims of keelhauling either died by bleeding out from injuries inflicted by barnacles on the hull of the ship or by drowning. Other forms of punishment ranged from being thrown overboard to being lashed to being marooned on a desert isle.
(Ireland marked 100 years of independence with a tourist route dedicated to a pirate queen.)
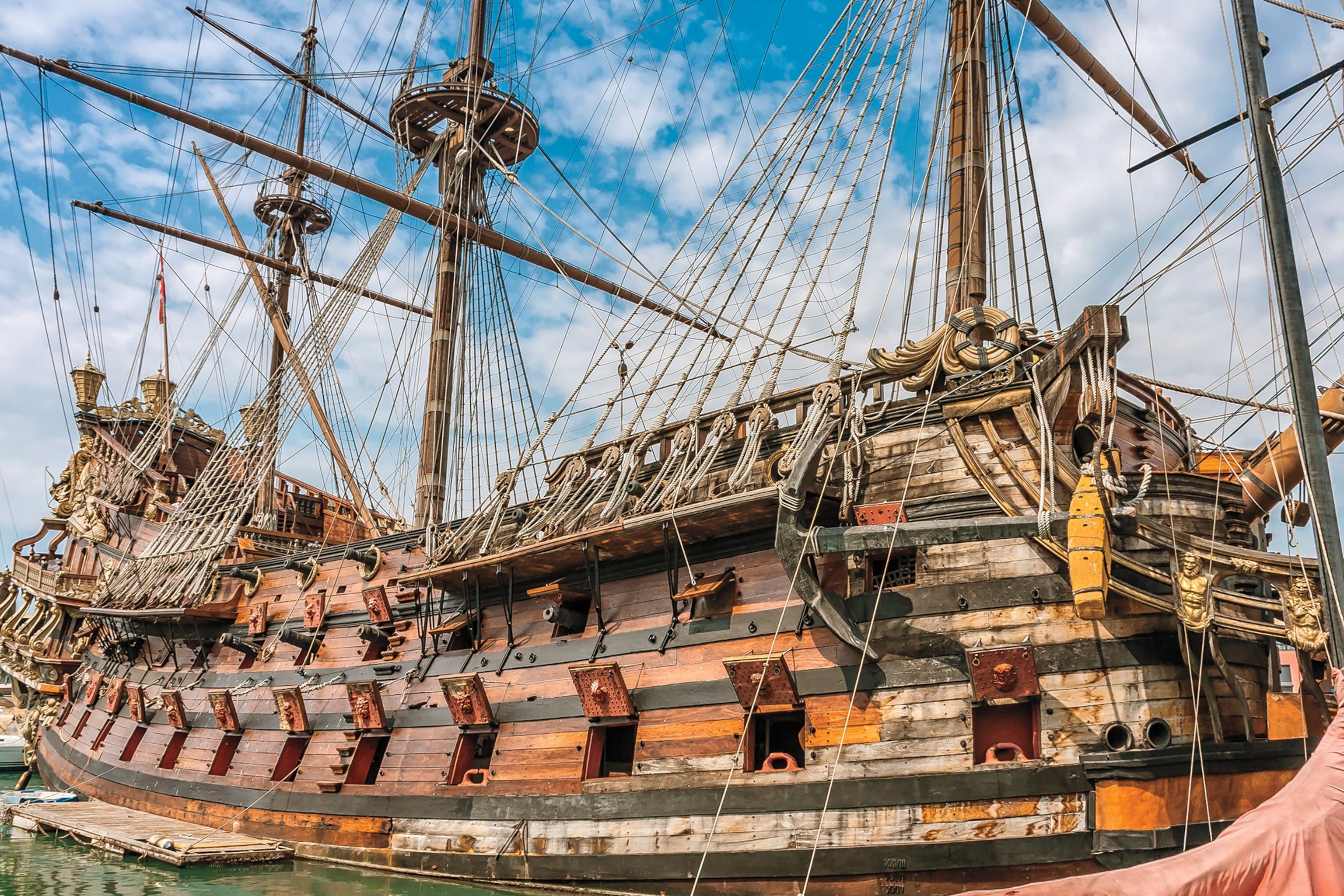
Pirate ships
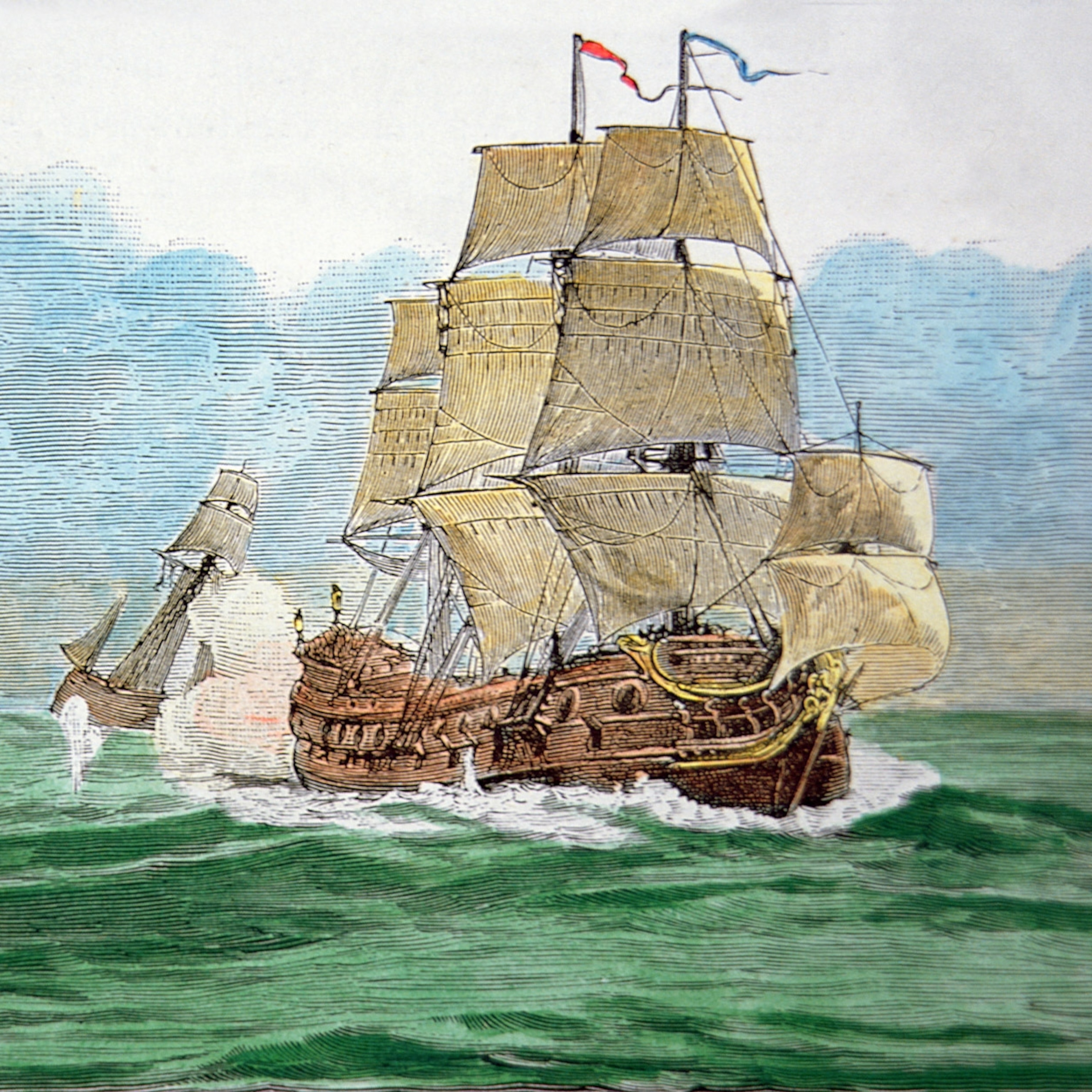
Most pirates did not sail Spanish galleons, or even the frigates such as Captain Jack Sparrow’s Black Pearl. They favored small, more maneuverable vessels, which allowed easy escape from larger warships that chased them. During the 16th and 17th centuries, sloops were the most common choice for pirates. They were quick and had a shallow draft, making easier escape into shallow waters. Schooners were another favorite of pirates. Similar to sloops, schooners were fast, simple to maneuver, and could easily hide in estuaries because of their shallow draft.
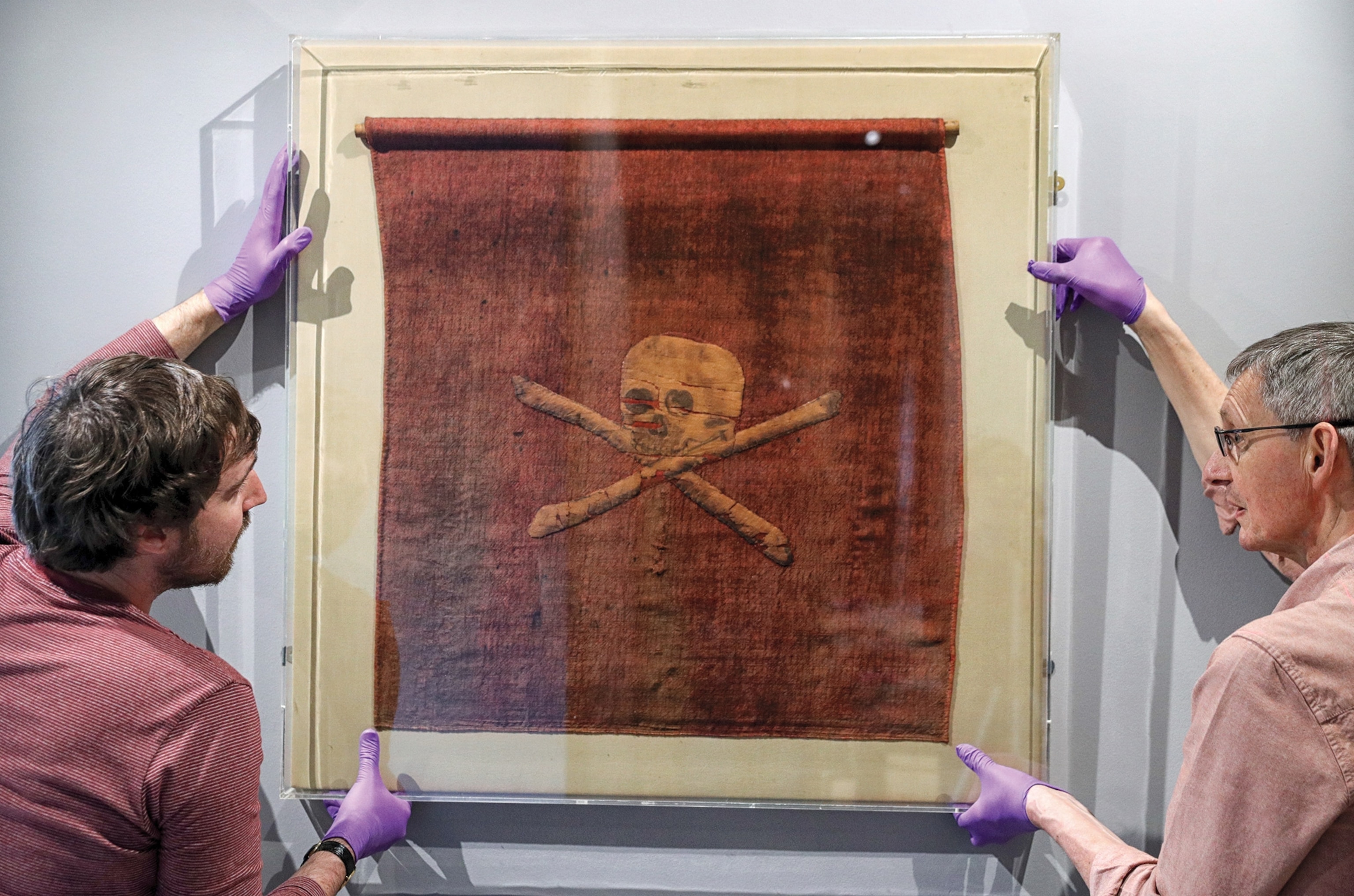
And, despite popular myth, most pirates did not fly the famous Jolly Roger—a skull and crossbones symbol on a black flag. Some flew a black flag, which meant the pirate was willing to give quarter, while a red flag meant blood and certain death. Blackbeard’s flag showed a skeleton holding a spear pointing at a bleeding heart. Pirate crews also often held the flags of several different nations so they could raise a particular flag to signal being “friendly” to a passing ship, only to raise their pirate flag once they were in close enough range to attack said vessel.
You May Also Like
Pirate fights
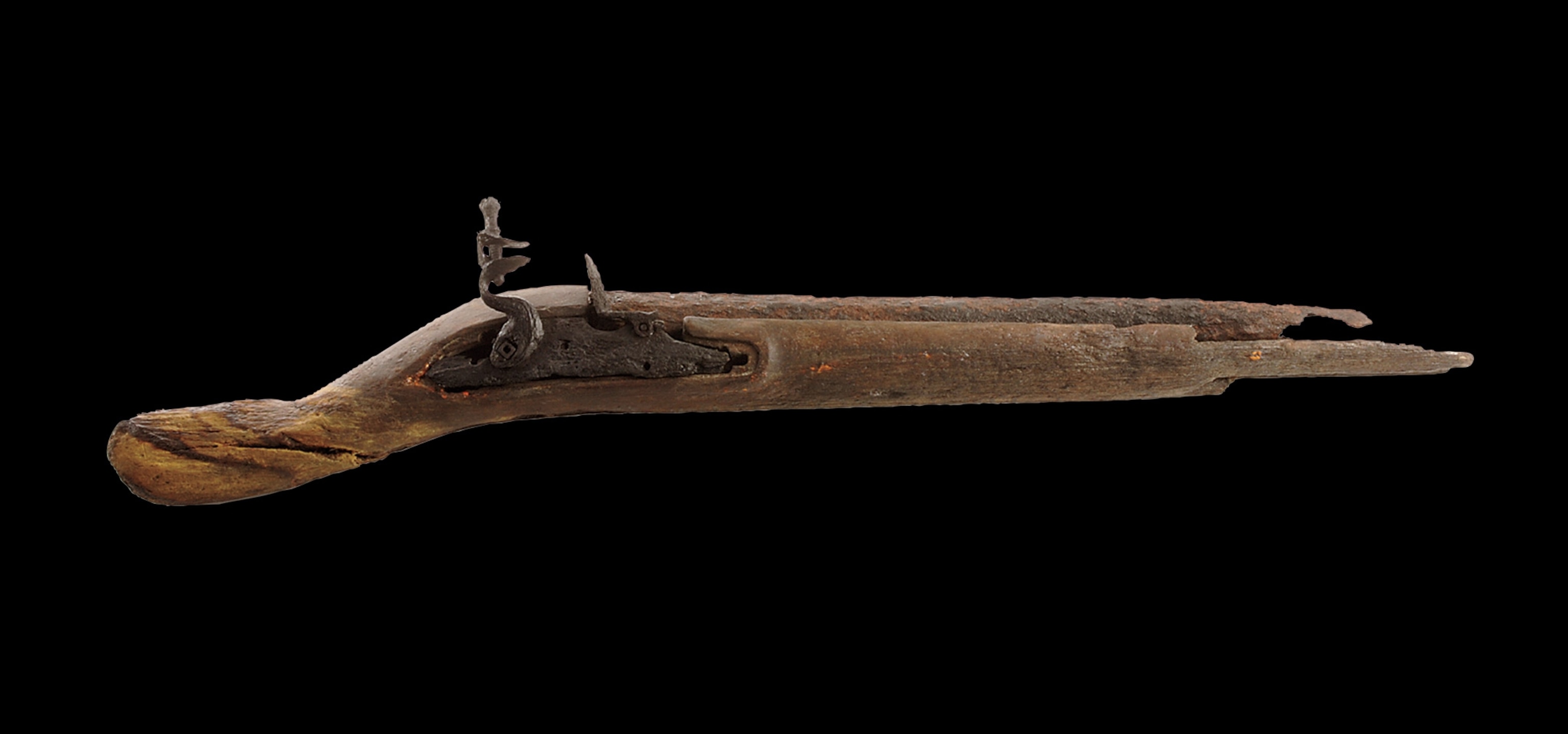
One thing that most of the pop culture depictions of pirates got somewhat right is that they liked versatile weapons. Cutlasses, short swords with a slightly curved blade, could be used to effectively fight in the confined areas of a ship and could also be used to butcher meat.
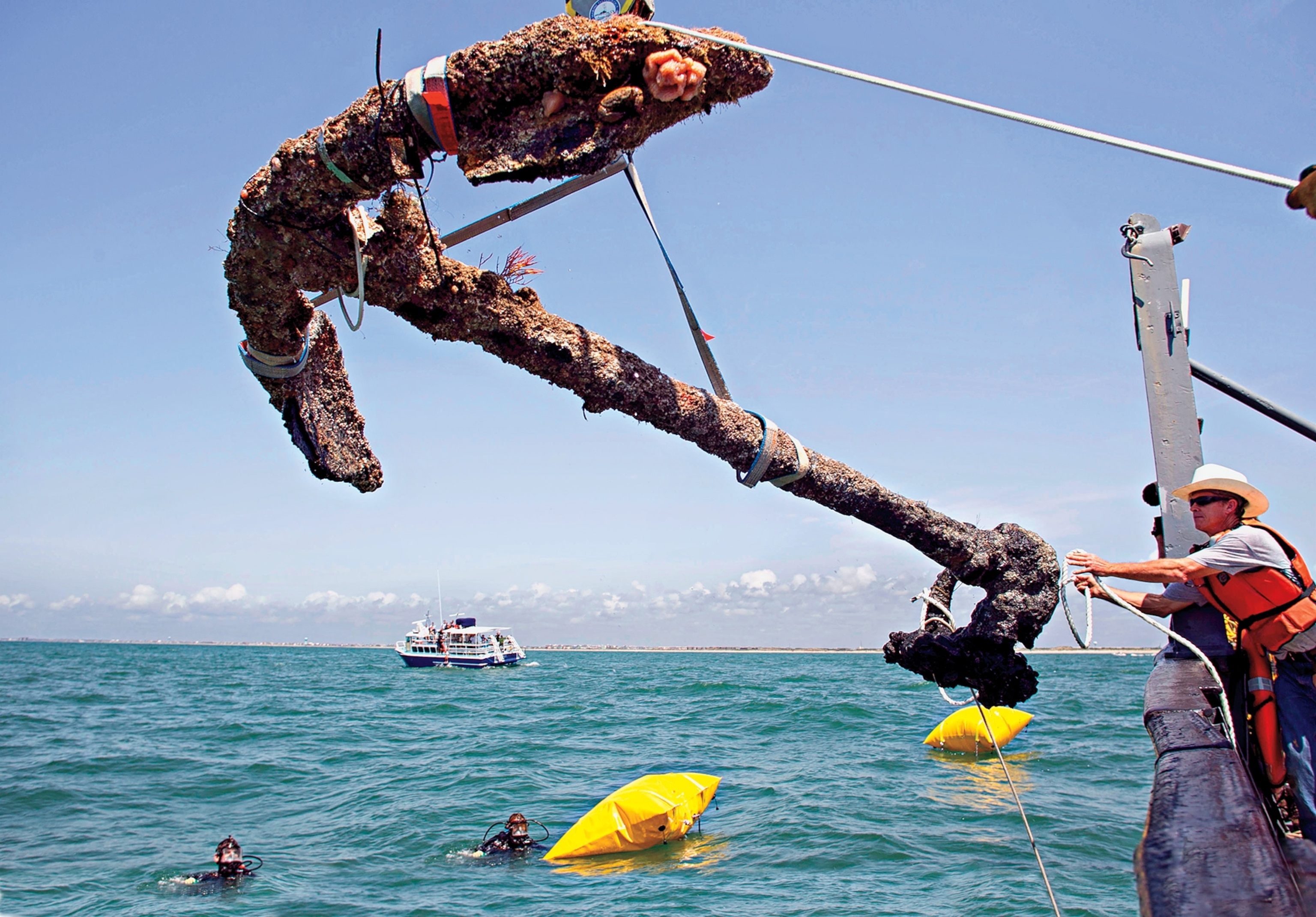
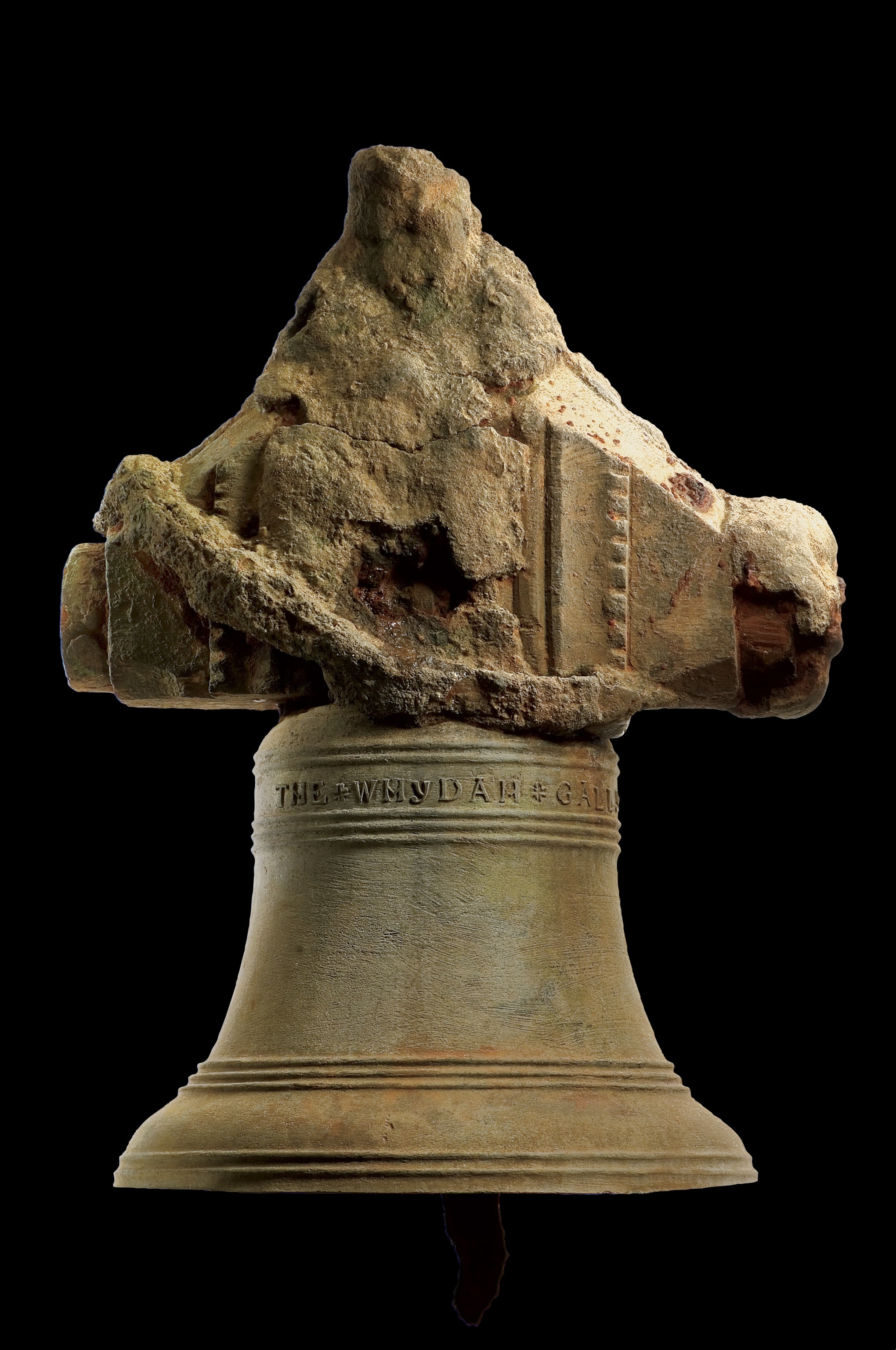
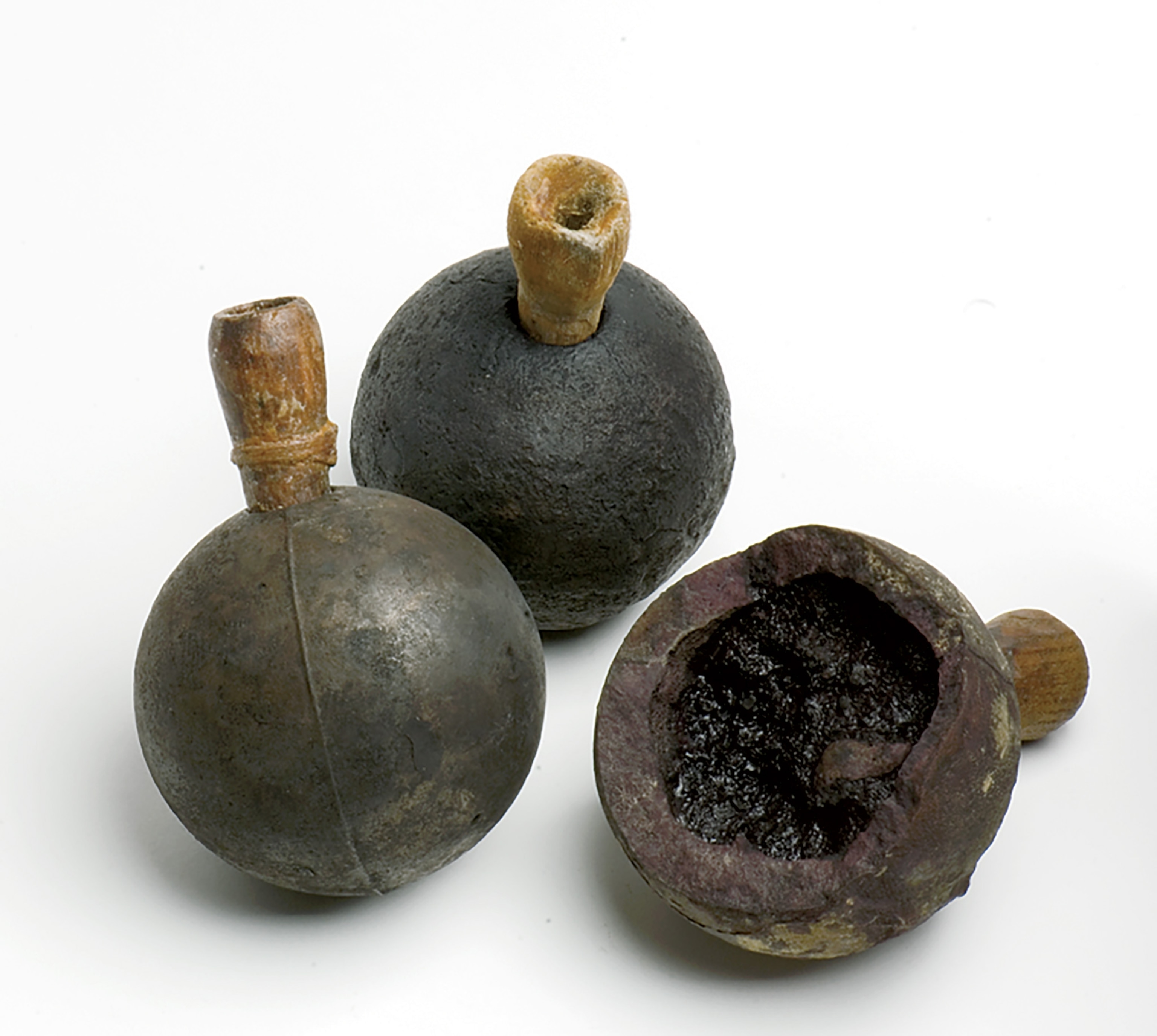
Artifacts from the 'Whydah Gally'
Pirates also enjoyed using a gun known as a blunderbuss. It had a distinct flared muzzle that sprayed small lead balls at intended victims. Cannons were also common onboard pirate ships. They could be loaded with chain shot (two cannonballs chained together), grapeshot (small cannonballs), or basic cannonballs. Their targets often didn’t stand a chance.
(Pirates once swashbuckled across the ancient Mediterranean.)
While books, movies, and popular culture may have taken liberty with descriptions of pirates through the ages, these pillagers have terrorized the seas for more than 2,000 years in one form or another, plundering victims and striking fear into their hearts. The most recent pirates work off the coasts of Somalia and Malaysia, looking far different from the “golden age” of piracy depictions. But one thing remains true: They are just as intimidating.

To learn more, check out Pirates. Available wherever books and magazines are sold.